AIR7310-B GNSS Guide¶
The AIR7310-B advanced software-defined radio (SDR) platform is equipped with a premium, industrial grade multi-band global navigation system (GNSS) receiver that provides nanosecond-level timing accuracy and performs anti-jam and anti-spoof countermeasures.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Connector Type | Front Panel SMA Connector |
| Crystal Oscillator | TCXO |
| Antenna | Active (3.3V DC Bias, 2-20mA Typ, active current limit ~70mA) |
| 1 PPS Accuracy | 5 ns to UTC |
| GNSS Reception Capability | GPS L1C/A, L5 QZSS L1C/A, L5 GAL E1B/C, E5a BDS B1I, B1C, B2a NavIC L5 GLO L1OF SBAS L1C/A: WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS, GAGAN |
| Anti-jam | Active CW detection and removal Dual onboard bandpass filters |
| Anti-spoof | Advanced anti-spoofing algorithms Galileo OSNMA |
| Horizontal Position Accuracy (CEP) | 1.5 m (standalone mode) |
Receiver Performance¶
| Parameter | Mode | GPS+GLO+GAL+BDS |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Tracking and Navigation | -167 dBm |
| Reacquisition | -160 dBm | |
| Cold Start | -148 dBm | |
| Hot Start | -157 dBm |
| Mode | Cold Start Acquisition | Hot Start Acquisition | Aided Start Acquisition | Max Update Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS+GLO+GAL+BDS | 24 s | 2 s | 2 s | 8 Hz |
| GPS+BDS+GAL | 25 s | 2 s | 2 s | 10 Hz |
| GPS+GAL | 29 s | 2 s | 2 s | 15 Hz |
| GPS+GLO | 26 s | 2 s | 2 s | 15 Hz |
| GPS+BDS | 28 s | 2 s | 2 s | 12 Hz |
| GPS | 29 s | 2 s | 2 s | 20 Hz |
Electronic Protection Against Interference and Jamming¶
The GNSS receiver on the AIR7310-B is capable of mitigating the negative impact of jamming signals. The receiver has active CW detection and removal, as well as dual onboard band pass filters to address this and maintain lock. In addition, the receiver has advanced anti-spoofing algorithms and Galileo OSNMA (Open Service Navigation Message Authentication) to ensure secure end-to-end transmissions from Galileo satellites to GNSS receivers.
1PPS Performance¶
| Parameter | Locked | Holdover (< 1 hour) | Holdover (< 24 hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1PPS Accuracy | <5 ns | <±180 usec | <±4.32 msec |
| 1PPS Stability (1-σ) | <4 ns | - | - |
Antenna Selection¶
Table 5 below details the supported GNSS constellations and their associated signals and center frequencies.
| GNSS | Signal | Center Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| GPS / QZSS | L1C/A L5 | 1575.42 MHz 1176.45 MHz |
| GLONASS | L1OF | 1602 MHz (15 Channels) |
| Galileo | E1-B/C E5a | 1575.42 MHz 1176.45 MHz |
| BeiDou | B1I B1C B2a | 1561.098 MHz 1575.42 MHz 1176.45 MHz |
| NavIC | SPS-L5 | 1176.45 MHz |
Table 6 below outlines the recommended dual band active antenna specifications for the supported GNSS signal types. The voltage to power the antenna pre-amplifier is superimposed (biased) on the antenna connector. In a deployment where multiple AIR7310-B radios are needed, only a single GNSS antenna is necessary.
| Parameter | Value | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Antenna Gain | 30dB (min) 40dB (max) | Including cable loss |
| Noise Figure | 3 dB | Including LNA (external or internal) |
| Group Delay Variation | 10 ns (max) | Inter-signal requirement 50 ns (max) |
| L1 Band Gain | 3 dBic | |
| L2/E5a Band Gain | 2 dBic | |
| L5/E5a Band Gain | 2 dBic | |
| Polarization | RHCP | |
| Axial Ratio | 2 dB max, at Zenith | |
| ESD Circuit Protection | 15 kV human body model air discharge | |
| Impedance | 50 Ohms |
Software Interface¶
GPSd Interface¶
AirStack provides software support for the GNSS disciplined oscillator via the GPSd service daemon. This allows for the AIR-T to leverage the system for position, Network Time Protocol (NTP), and many other common features for GPS.
A full list of the GPSd manual pages that describe the operation may be found here. For example, to dump the raw NEMA message to the terminal screen, use the command:
$ gpspipe -r
To view the GPS data stream output in a table, use the command
$ gpsmon
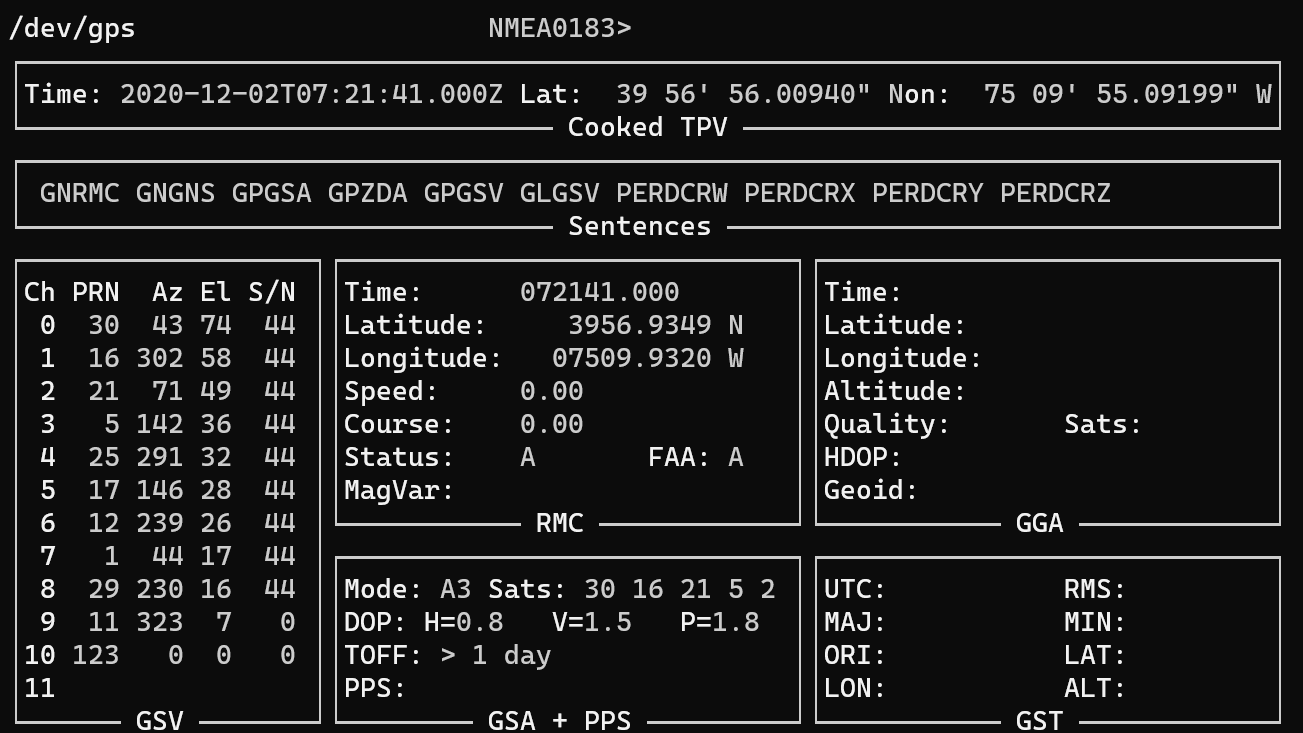
GNSS as the Reference¶
The SoapyAIRT driver in AirStack can easily leverage the GNSS disciplined oscillator as a frequency reference. This may be done by setting the clock source to GPS using the setClockSource method:
sdr = SoapySDR.Device(dict(driver="SoapyAIRT"))
try:
sdr.setClockSource("GPS")
except RuntimeError as e:
print("GPS Clock Reference Failed!")
print(e)
sdr.setClockSource("internal")
For more information, see the External Clock Reference application note.