Receiving Samples with Rust¶
In this tutorial we show you how to perform basic functionality with the AIR-T using Rust. You will learn how to interact with the AIR-T radio drivers, stream signal data from the radio, and create a one-time plot of the wireless spectrum. The AIR-T does not come preloaded with rust, so you will need to install it yourself first. The recommended solution is to install it in a conda environment. Below you will find the steps to install and the source code.
Compatibility¶
If you are running Airstack 1.X or earlier we recommend installing rust using a conda environment. You can find the instructions to do this here.
Installing Rust on the AIR-T¶
Default Package Manger:¶
- Rust may be installed using rustup with the commands below:
curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh source "$HOME/.cargo/env" -
When working with soapysdr from rust you may also need to install some additional packages:
apt install libclang-dev llvm-dev pkg-config -
To verify your installation, activate your conda environment and then run the commands below:
rustc --version cargo --version
Rust Code¶
- Set up a new project in rust using cargo:
cargo new hello_world -
Add the following packages to your cargo.toml file:
[dependencies] num-complex = "0.4.3" soapysdr = "0.3.2" plotly = {version = "0.8.3", features = ["plotly_ndarray"]} ndarray = "0.15.0" rustfft = "6.1.0" -
The source code to receive samples is below. You will need to copy this into your rust source code directory:
use ndarray::Array;
use num_complex::Complex;
use plotly::common::Title;
use plotly::layout::{Axis, GridPattern, Layout, LayoutGrid};
use plotly::{Plot, Scatter};
use rustfft::FftPlanner;
use soapysdr::Direction::Rx;
fn main() {
// Data transfer settings
let rx_chan = 0; // RX1 = 0, RX2 = 1
let N: usize = 16384; // Number of complex samples per transfer
let fs = 31.25e6; // Radio sample Rate
let freq = 2.4e9; // LO tuning frequency in Hz
let use_agc: bool = false; // Use or don't use the AGC
let timeout_us: i64 = 5_000_000;
let rx_bits = 16; // The AIR-T's ADC is 16 bits
// Setup Device
let dev = soapysdr::Device::new("driver=SoapyAIRT").expect("failed to open device");
// Set Sample Rate
dev.set_sample_rate(Rx, rx_chan, fs)
.expect("failed to set sample rate");
// Check Sample Rate
let sample_rate: Result<f64, soapysdr::Error> = dev.sample_rate(Rx, rx_chan);
println!("Sample rate set to: {}", sample_rate.unwrap());
// Set Gain Mode
dev.set_gain_mode(Rx, rx_chan, use_agc)
.expect("failed to set gain mode");
// Set Frequency
dev.set_frequency(Rx, rx_chan, freq, ())
.expect("failed to set frequency");
// Create data buffer and start streaming samples to it
let mut rx_stream = dev.rx_stream::<Complex<f32>>(&[rx_chan]).unwrap();
//Create complex array of length N
let mut rx_buff = vec![Complex::new(0., 0.); N];
// Activate Stream
rx_stream.activate(None).expect("failed to activate stream");
// Read Samples
let rt = rx_stream
.read(&[&mut rx_buff[..]], timeout_us)
.expect("read failed");
// Deactivate Stream
rx_stream.deactivate(None).expect("failed to deactivate");
println!("Length of the array read: {rt}");
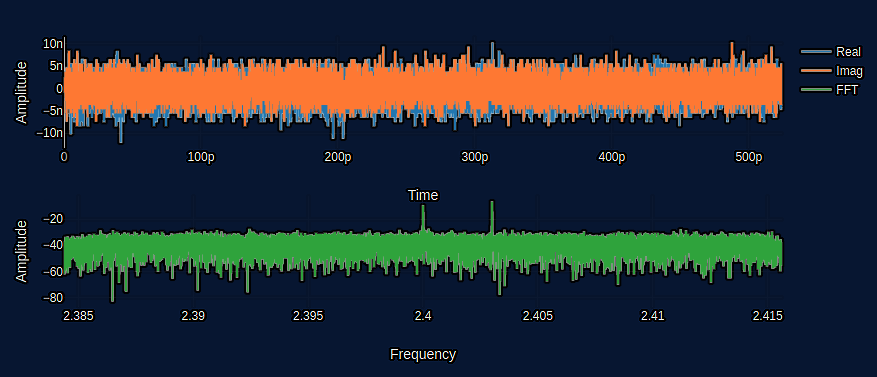
//Plot Data
// Split real vs imag and normalize [-1, 1]
let n = 2.0_f32.powi(rx_bits - 1);
let r_real: Vec<f32> = rx_buff.iter().map(|v| v.re / n).collect();
let r_imag: Vec<f32> = rx_buff.iter().map(|v| v.im / n).collect();
// FFT
let mut planner = FftPlanner::<f32>::new();
let fft = planner.plan_fft_forward(N);
fft.process(&mut rx_buff);
let mut fft_vals: Vec<f32> = rx_buff.iter().map(|v| 20. * (v.norm()).log(10.)).collect();
// Shift Array
fft_vals.rotate_right(N / 2);
// create time and freq arrays
let num_samp = N as f64;
let time_us = Array::range(0., num_samp, 1.) / fs / 1e6;
let f_ghz = (freq + (Array::range(0., fs, fs / num_samp) - (fs / 2.) + (fs / num_samp))) / 1e9;
// Setup Plots
let mut plot = Plot::new();
let layout = Layout::new()
.grid(
LayoutGrid::new()
.rows(2)
.columns(1)
.pattern(GridPattern::Independent),
)
.y_axis(Axis::new().title(Title::new("Amplitude")))
.x_axis(Axis::new().title(Title::new("Time")))
.y_axis2(Axis::new().title(Title::new("Amplitude (dBFS)")))
.x_axis2(Axis::new().title(Title::new("Frequency (GHz)")));
plot.set_layout(layout);
// Plot I/Q
let trace_re = Scatter::new(time_us.to_vec(), r_real)
.name("Real")
.x_axis("x1")
.y_axis("y1");
let trace_im = Scatter::new(time_us.to_vec(), r_imag)
.name("Imag")
.x_axis("x1")
.y_axis("y1");
plot.add_trace(trace_re);
plot.add_trace(trace_im);
// FFT Plot
let trace_fft = Scatter::new(f_ghz.to_vec(), fft_vals)
.name("FFT")
.x_axis("x2")
.y_axis("y2");
plot.add_trace(trace_fft);
plot.show();
}
Output Plot¶